In the web development land, there is a new buzzword called "JAMstack".
JAM stands for Javascript API Markup.
Websites built using JAMstack technologies is supposed to be "blazing fast". Popular websites built on JAMstack includes React official documentation, freeCodeCamp, Impossible Foods
...
When I first came across "JAMstack", and after reading up on it, I was left scratching my head. I understand every word in those articles, the technology sounds cool, but I don't understand a thing.
It takes me a while to get my head around it. So, lets see if I can explain it.
In essence, a JAMstack website is rendered at compile-time, and has pre-built static assets served ready via CDN; To be considered a JAMstack app, the HTML needs to be served statically, which basically means not being dynamically rendered from a server.
So the key words here are "pre-built/pre-compiled".
...
To understand this better, we need to go back to the history of web.
1)
Long ago, each time user goes to a page in our website (e.g. /about.html), the web server renders and serves the appropriate files back to the browser.
Each time, a new GET request is sent to the server, which responds with a new document, completely discarding the old page altogether. Hence if you move from index.html to about.html, you will see the whole page loads again.
2)
Not too long ago, a new trend called Single Page Application (SPA) took over. With the helps of client-side JavaScript libraries such as React, jQuery, Angular, our browser makes only the first request to our web server.
Subsequent navigation is handled by JavaScript on our browser, and when user goes to different pages, the browser renders the right content dynamically. User experience is smoother and faster.
3)
Recently, there are growing number of web apps that are part of the isomorphic / universal app architecture, e.g. MERN stack for React + Node application. There are also specific frameworks such as Next.js that help SPA with server-side rendering (SSR) to increase performance, especially SEO optimisation.
In a SSR setup, we need an Application Server e.g. Node.js server to dynamically render HTML documents at run-time.
4)
JAMstack is the latest kid to the block.
With JAMstack, webpages are technically server-side rendered too, but it is rendered at compile-time and pre-served, instead of render dynamically at run-time.
The assets are served without any run-time processing on server side.
- compile or build time means these steps are run on a server somewhere (e.g. on Netlify server), far ahead of time when you build the app
- run-time means these steps are run when user is accessing the site on browser
Think of it as when you are buying fruit juice, an isomorphic app will have a server blend the fruits on the spot and serve you the drink, but a JAMstack vendor will just hand you the drink ready-made.
The benefit here is apparent: it is blazing fast, and it doesn't require a guy mixing the juice all the time in the background.
...
What is JAMstack good at
It is especially good for read-heavy websites where content are more static, e.g. blog, e-commerce, magazines, documentation, etc.
What is JAMstack not good at
For web apps with very dynamic or high amount of personalised content - e.g. social media, chat apps - an isomorphic app can do the job better.
Not exactly static
Even though JAMstack serves static assets well, it doesn't mean the web app is "static".
You can have client-side rendering and run-time data fetching as well. After static files are served from CDN, you can re-hydrate the React on the page on client-side and it works like a normal React SPA.
...
What does JAMstack technologies entail?
A popular framework in this space is Gatsby JS. It uses React and GraphQL.
Gatsby supports different content source, e.g. Wordpress, Contentful, or other headless CMS.
For delivery, you can use Netlify, AWS S3, or even Github Pages.
Gatsby does many things at build time to generate static assets, e.g. GraphQL queries to get data from filesystem, external API, or a database.
...
Diagrams
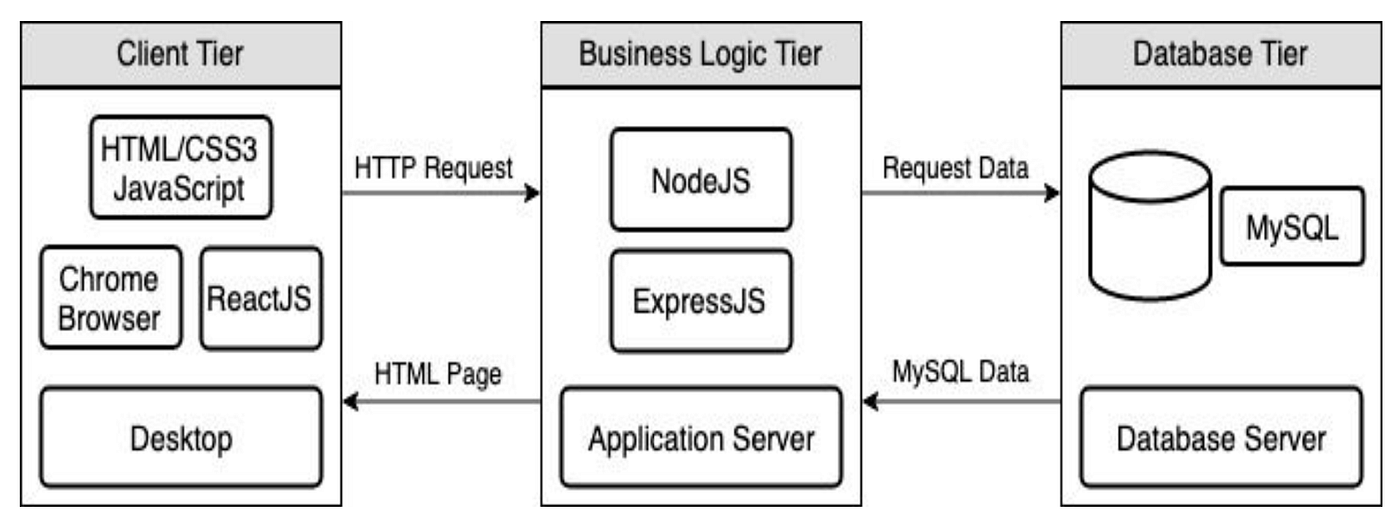
MERN stack isomorphic app. Credit to Calvin Nguyen article on Medium
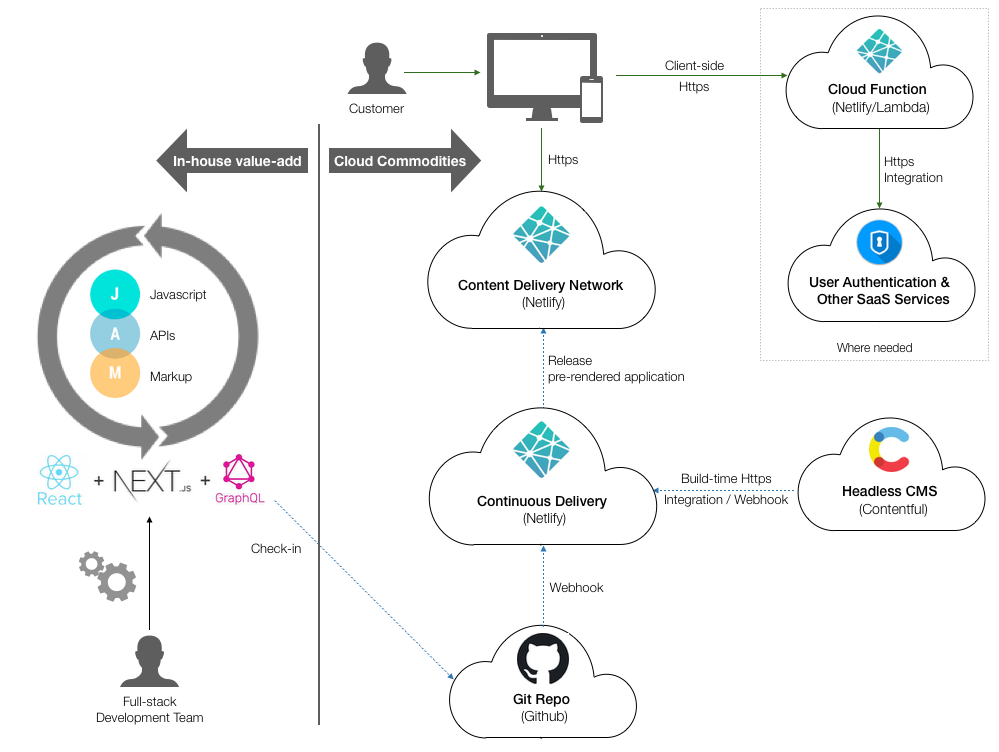
JAMstack architecture. Credit to Mike Carlisle on hackernoon
...Further notes
This blog is built with Gatsby and Netlify; I will document my experience in more details in a separate post.
Good article by Josh Comeau
Another article